Microsoft And Sunseap Sign Agreement On Largest-Ever Solar Project In Singapore
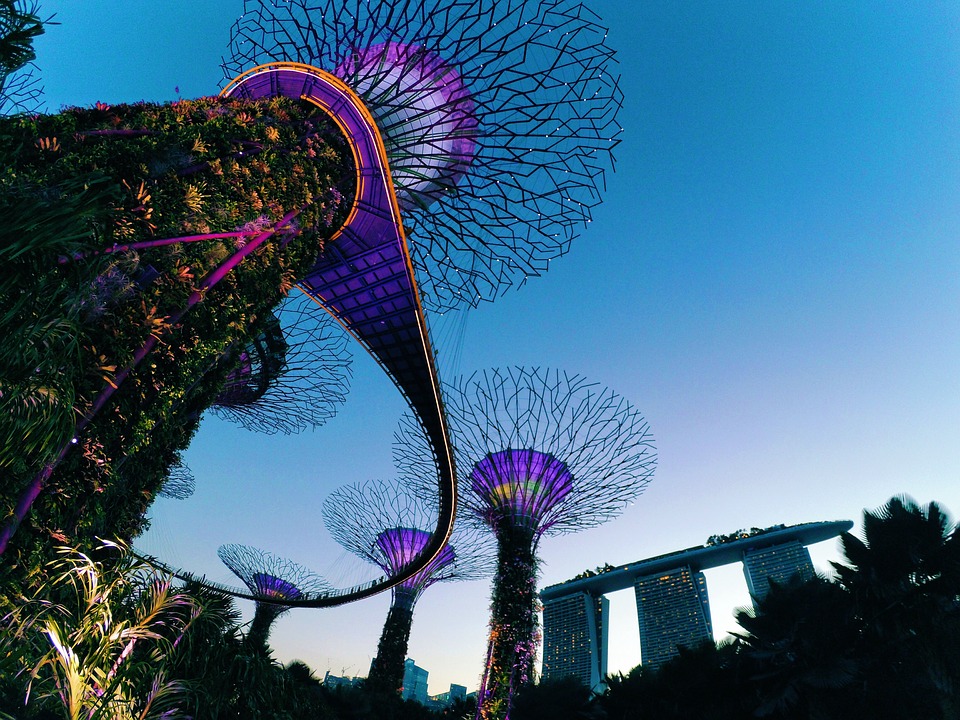

Microsoft Corp. recently announced a new agreement with Sunseap Group that marks Microsoft’s first clean energy deal in Asia and will create the single-largest solar energy portfolio in Singapore to […]
HVACR Vietnam 2018 Introduces Green Building And Energy Efficiency

HVACR Vietnam is excited to be hosting its latest edition in Hanoi, after 11 previous editions in Ho Chi Minh City. Local & International Exhibitors This year, the event will […]
BuildTech Yangon Synergises Green Network Development in Myanmar

The 4th edition of BuildTech Yangon concluded on 20 May 2017 after three days of industry discussions, international dialogues, commercial engagements and knowledge sharing in Myanmar. Organised by Sphere Exhibits, […]
COGfx Study Shows Better Thinking, Better Health in Green-Certified Buildings

Considering all the time we spend at work, have you ever wondered if the building you are working in is healthy? Or, could make you think better, or be more […]
Can your building environment affect the way you think and perform?

We know green buildings conserve natural resources, minimize environmental impacts and improve the indoor environment, but do you know it can also positively affect your cognitive performance? A recent study […]
Eco Expo Asia 2016

The 11th edition of Eco Expo Asia takes place at AsiaWorld-Expo in Hong Kong from 26-29 October, with the theme being “Green Solutions for a Changing Climate”. The expo is […]
GreenUrbanScape Asia 2017

Asia is home to the world’s fastest growing cities. With the region’s increasing urbanisation, the global search for urban design, landscaping and greenery to create spaces that are conducive for […]
Shanghai Intelligent Building Technology 2015

Following its success at the 2014 show, the 8th Shanghai Intelligent Building Technology will continue its goal of providing a top regional platform for China’s rapidly growing intelligent building market […]
Green Building & Retrofits Expo Asia 2015

Green Building & retrofits (GBR) Expo Asia 2015, the 5th international Exhibition & Conference on Green Building & Retrofits held in Thailand for the Asia Market. There will be showing […]
Clean and Renewable Energy
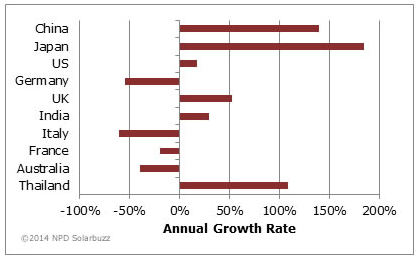
Solar Photovoltaic (PV) is perhaps the first thing that comes to people’s minds on the subject of clean renewable energy. PV technologies convert energy from sunlight into direct current (DC) […]
Solar PV Systems bring green energy for buildings

[av_textblock size=” font_color=” color=”] Most solar PV systems are installed on buildings or mounted on the ground, if land is not a constraint. In the following case studies, we look […]
Promising outlook for Guangzhou Electrical Building Technology 2015 with impressive exhibitor numbers
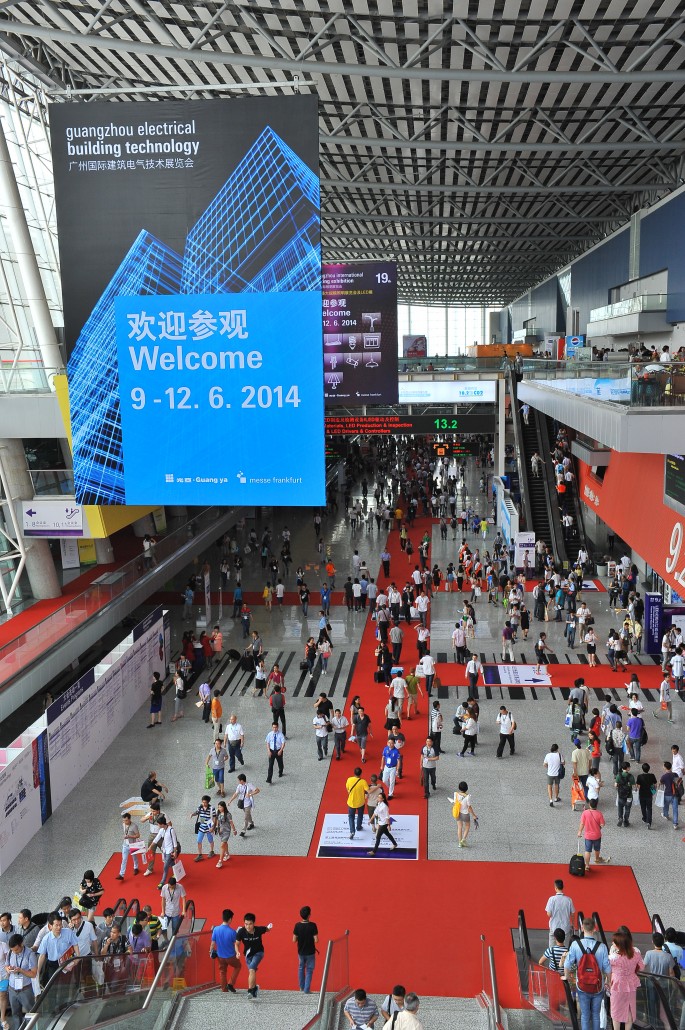

The 12th edition of Guangzhou Electrical Building Technology will be held from 9 – 12 June at the China Import and Export Fair Complex in Guangzhou, China. The four-day event […]
Big Ass Fans expands into South and Southeast Asia with Singapore subsidiary
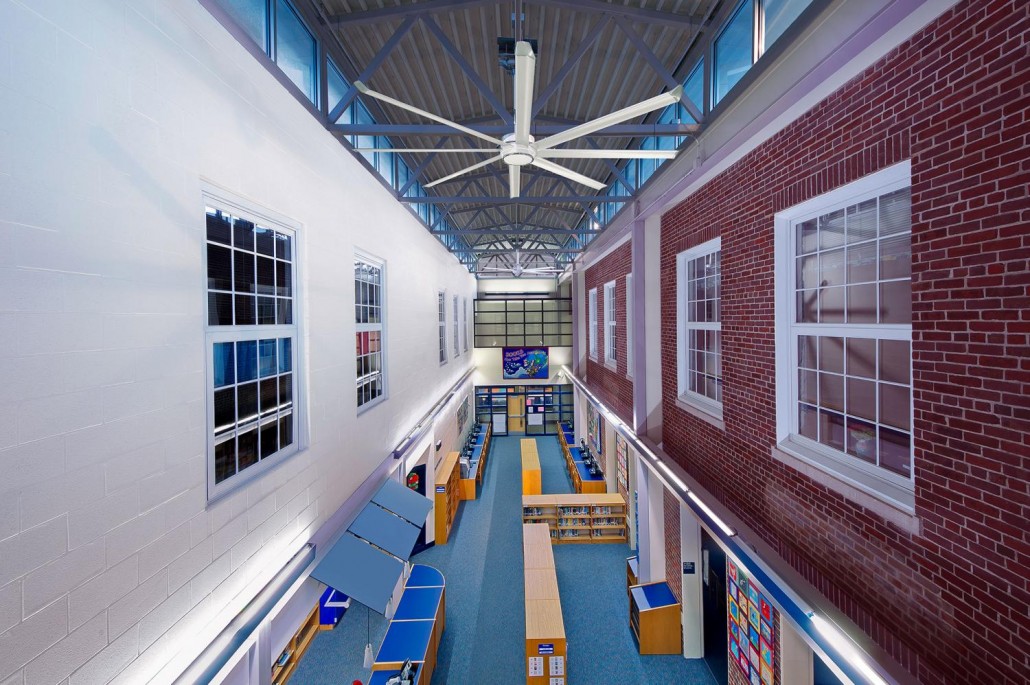

SINGAPORE — US-based Big Ass Fans, the world’s largest manufacturer of energy efficient fans, continues to expand globally and is now better serving the South and Southeast Asia markets via […]
Zuellig building named winner in uli global awards for excellence
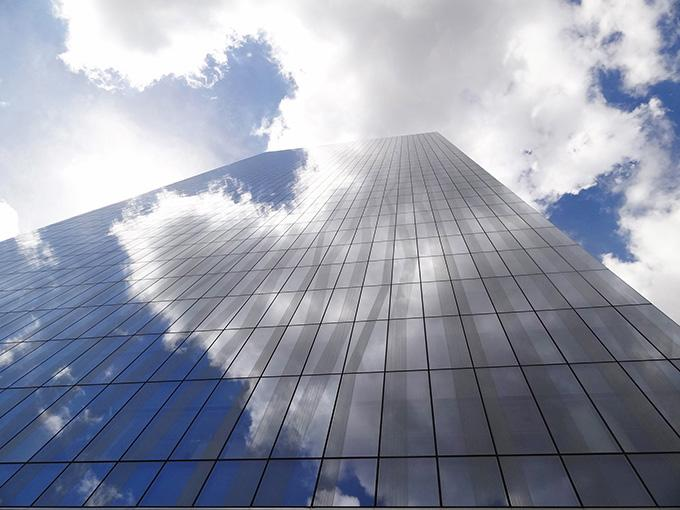

PHILIPPINES, MANILA – The Zuellig Building, an elegant office tower located in Manila, Philippines, was selected as a winner in 2014 Urban Land Institute (ULI) Global Awards for Excellence program. […]


